
Dot matrix LED display panels are display devices composed of arranged light-emitting diodes (LEDs), and it is commonly found in everyday applications, from bus stop annunciators, traffic lights to subway route maps, bulletin boards, and so on.
In this article, let's learn more about LED matrix displays.
What is a RGB dot matrix display panel
RGB matrix panels are lighting devices that use the combination of red, green and blue light-emitting diodes (LEDs) to create a wide range of colors and effects, with noticeable spacing between each LED light when viewed up close.
RGB matrix panels can produce a wide array of colors using the three basic colors in different ratios, a significant advantage over traditional lighting solutions that typically emit a single fixed color.
Highly flexible and creative, they work well as fill light or background light to generate varying appealing effects and scenes, such as flashing, scrolling, smoothing, fading, and music synchronization.
What is the pixel of an LED display?
A pixel is the smallest imaging unit of a display screen, typically composed of one or more light-emitting diodes (LEDs). For example, the typical display screen design scheme, like the term "2R1G1B", indicates that a pixel is composed of 2 red LEDs, 1 green LED, and 1 blue LED.
How does LED matrix displays work?
LED matrix displays work by arranging multiple light-emitting diodes (LEDs) in a grid pattern. The control chip receives external signals and converts them to the appropriate voltage and current to control each LED. By selectively controlling the states of these pixels, they can together showcase various text, graphics or animation.
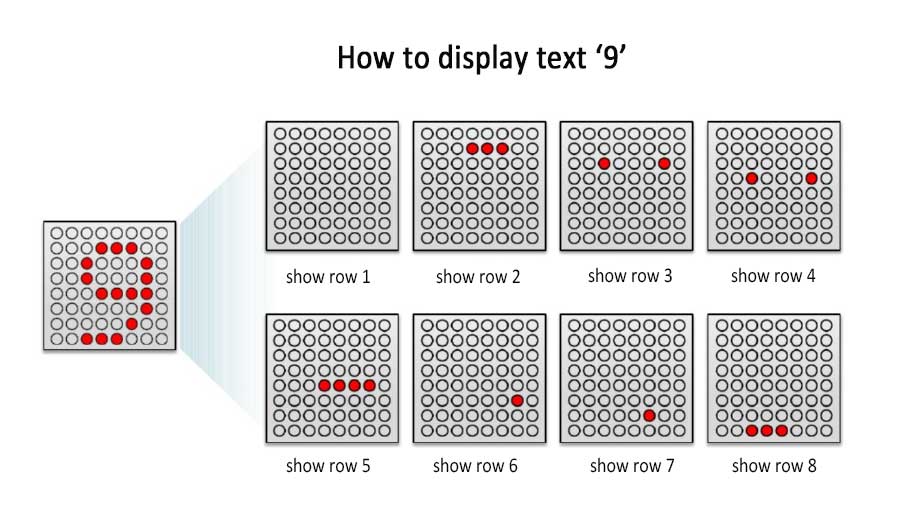
The LED display utilizes a dynamic row-by-row or column-by-column scanning mode at a very swift frequency. That said, only one row or column is lit at any given moment.
In this working mode, the LED display lights up row by row, with only one row illuminated at a time. However, as long as each row can be lit up more than 50 times per second( namely a refresh rate higher than 50 Hz), human eyes would perceive a stable full-screen image due to the persistence of human vision effect.
Taking an 8x8 matrix as an example, there are a total of 64 LEDs arranged on the panel, with each LED placed at the intersection of a row line and a column line. Sequentially illuminate each row of LED lights for 4 milliseconds and then turn them off. When reaching the last row, repeat the process starting from the first row. This speed is fast enough for the human eye to perceive that all 8 rows of LEDs are lit up at the same time, as a result, the end result presented is stable and complete messages.
Advantages and disadvantages
Compared to incandescent lamps or fluorescent bulbs, LED lighting consumes less electricity and generates less heat. Plus, LED bulbs neither contain mercury nor have fragile glass components, working at low operational voltage, without warm-up time needed.
Matrix display panels are widely used for the following reasons:
- High Brightness. LED dot matrix screens use LEDs as display elements, providing high brightness and strong luminosity.
- Low power Consumption. LED dot matrix screens can be driven with lower voltage and current, resulting in energy savings. In fact, an LED bulb will actually use 75% less energy on average compared to a standard fluorescent bulb.
- Ease of Control. LED dot matrix screens are controlled through control chips or drivers, making operation simple and convenient. Plus, they can be remote controlled via app, or voice instructions.
- Customizability. LED dot matrix screens can be customized in terms of size, pixels, and shape to suit various applications, such as cylindrical screens, stepped screens, and flexible screens.
- Long lifespan. The lifespan of LED bulbs is approximately 50,000 hours, with some lasting up to 100,000 hours. An LED bulb can last about 14 years if used for 10 hours a day.
- Simple design and low maintenance. LED dot matrix screens have strong resistance to vibration and interference, suitable for harsh working environments. Plus, each pixel is independent, therefore destruction or degradation of a single LED light will not affect the others.
- Easy scalability. They can be easily scaled to different sizes without major design changes, allowing for innovative lighting designs or flexible applications.
Apart from the advantages, LED displays do come with some disadvantages, including:
- Light Pollution. To ensure visibility during the day, LED displays tend to generate higher brightness, resulting in light pollution. To mitigate this issue, consider adding light sensors to automatically adjust the brightness to the surrounding environment.
- Expensive. LED displays are more expensive compared to traditional lighting. The technology involves costs such as LED panels, control systems, and PCB design, making it relatively expensive.
- Prone to defects. LED displays are more prone to defects and damage, such as shifted color, partial lit or flashing. Proper engineering design and maintenance are essential to prevent such issues.

Types of RGB matrix display
Based on used LED colors, RGB matrix displays fall into one of three categories: single-color, two-color, and full-color.
Single-color matrix display
The luminous pixels composing single-color LED screen emit only one color, typically either red, orange or green. Blue LEDs are generally reserved for full-color screens due to the relatively high cost.
Bright and inexpensive, single-color screens are suited for displaying simple text messages, working well as billboards, electronic clocks, timers, elevator screens, etc.
Two-color matrix display
A Two-color LED display screen typically consists of red and green LED lights, allowing it to display a total of 65,536 colors in theory(256 x 256 = 65,536).
While failing to achieve the full-color display effect, two-color displays are still widely used in displaying text, images, animations, and video images.
Cost-effective and expressive, dual-color displays are widely seen in numerous spots such as sports stadiums, traffic signal lights, train stations, subway stations, etc.
Full-color matrix display
Full-color LED displays utilize a combination of red, green, and blue LED lights to present various colors and appealing dynamic effects. Each LED light internally integrates light-emitting diodes in three colors: red, green, and blue.
By combining different grayscale levels of these three basic colors, a full-color display can reproduce natural colors more effectively. In theory, it can produce 256256256 colors, covering almost all colors distinguishable by the human eye.
How to choose a suitable LED RGB matrix display
Whether planning to buy a standard LED screen or a customized LED matrix panel, there are some features worth consideration to help you make an informed choice. Don't worry, they easy to understand and identify, let's jump into them.
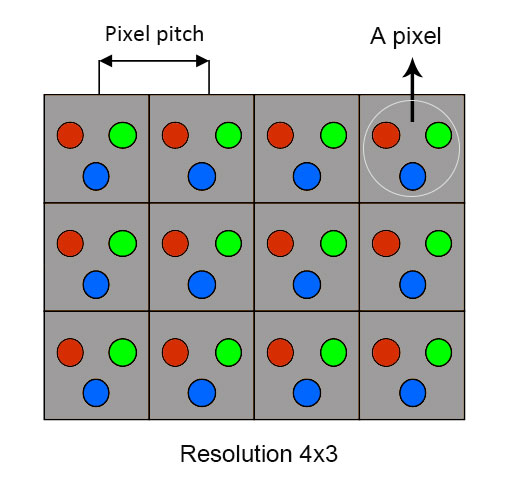
Pixel pitch
Pixel pitch, sometimes referred to as dot pitch, refers to the distance between the centers of two adjacent LED pixels, measured in millimeters. This value indicates the pixel density in a given area and typically ranges from 1 mm to 50 mm. It is usually abbreviated by a "P" next to a number. For example, P5 refers to a pixel pitch of 5 millimeters.
A higher value indicates a larger space between each pixel. The larger the pixel pitch, the farther the audience must stand to appreciate a clear picture without noticing the spaces between pixels. Conversely, smaller values imply a closer spacing between pixels, leading to higher pixel density and resolution.
Pixel pitch is directly tied to image clarity and cost. For instance, when the pixel pitch is down from 4mm to 2mm, both the pixel count and resolution double, resulting in higher price.
In some cases, having a smaller pixel pitch doesn't necessarily translate to a better LED display, it simply means that viewers can sit closer to the screen. Matching pixel pitch to viewing distance helps ensure an optimal viewing experience.
Larger pitches make LED walls more suitable for situations where viewing occurs from a greater distance, such as digital billboards, stadium screens or concert signage, even though they may not be as visually appealing up close.
As a general rule of thumb, the optimal viewing distance is typically 2-3 times the pixel pitch (in meters). For example, for a P2 full-color LED display screen,the suitable viewing distance is 4-6 meters.
| Pixel pitch | Minimum viewing distance | Best viewing distance |
|---|---|---|
| P1.53 mm (Indoor display) | > 1.53 meters | > 4.6 meters |
| P2 mm (Indoor display) | > 2 meters | 6 meters |
| P3 mm (Indoor display) | > 3 meters | 9 meters |
| P4 mm (Indoor display) | > 4 meters | 12 meters |
| P5 mm (Indoor display) | > 5 meters | 15 meters |
| P10 mm (Outdoor display) | > 10 meters | > 30 meters |
Viewing angle
Viewing angle refers to the position from which a viewer can see the image clearly. Since the LED emits light in a cone-shaped pattern, it affects the audience's overall perception of the content in different viewing angles. For screens with smaller viewing angles, you need to position yourself directly in front of the screen to see a clear image.
Generally, angles below 60 degrees are considered narrow viewing angles, those between 60 and 120 degrees are defined as wide viewing angles, and angles exceeding 120 degrees are considered ultra-wide viewing angles. The size of the viewing angle directly determines how many audiences a screen can reach, in most cases, the bigger the better.
For situations requiring long-time viewing and high brightness, narrow-angle LED displays are more suitable for notification screens or highway warning displays. Wide-angle LED displays are better options for advertisements and promotional information in high-traffic areas like shopping malls, sports events, and more.
Brightness
The brightness of an LED display refers to the luminous intensity per square meter when the display is functioning normally, measured by cd/㎡ or nit(s). The higher the value, the brighter the display. The brightness of an LED display plays a crucial role in the visibility of content.
On the other hand, other optical parameters (like contrast, color saturation, and grayscale) can only be perceived when the screen operates at a sufficient brightness. This is easy to understand, if the LED display is at an extremely low or high brightness, it makes no sense for color saturation or grayscale.
Is a brighter monitor always a better display? Clearly No. excessive brightness or too low brightness both cause eye fatigue and headaches.
How much brightness does an LED screen need? It largely depends on your project's needs and use cases. Here we have compiled a table of brightness recommendations for different usage scenarios
| Context | Recommended display brightness |
|---|---|
| Indoor | 300 to 2,500 nits |
| Semi-outdoor | 2,500 to 5,000 nits |
| Outdoor | 5,000 to 8,000 nits |
| Outdoor in direct sunlight | Above 8,000 nits |
In addition to the above mentioned parameters of LED itself, a few external factors should be kept in mind, including display purposes, installation environment, audience viewing habits, your budget, etc.
Common issues and maintenance
When developing LED matrix panels, there are some common issues you may encounter. For example, if the display duration is too brief, the brightness may be insufficient, conversely, if the duration is too prolonged, flickering may be noticeable.
Below are some of these problems and solutions:
Blurry or distorted display content
This issue may be caused by inappropriate drive currents or interference with control signals. Try adjusting the size of the drive current to get the LEDs work properly. Additionally, check whether the control signal lines are in contact with other sources of interference. It may be necessary to isolate or rewire them if interference is detected.
Inaccurate or shifted display colors
For inaccurate or shifted colors, it may be due to calibration errors or inconsistent quality of the LED beads. Try color calibration or replace any defective/inconsistent LED beads as needed.
Partial LEDs not lit or flashing
If some LEDs are not lit or flashing, it could be due to poor connections or damaged LEDs. First, check if the connection lines are secure and ensure good contact. If the problem persists, consider replacing the damaged LEDs.
Unable to update or stalled display content
If the LED matrix panel cannot update or display content, or gets stuck in a certain state, there may be a fault in the control chip or driver. Try reconnecting the power or restarting the control chip. If the issue persists, you might need to replace the faulty control chip or driver.
Related Questions
What is the difference between LED display and LCD display?
LCD stands for Liquid Crystal Display, technically, both are liquid crystal displays. In fact, LED displays are a subset of LCDs, and LED displays are upgraded version of LCD. All LED monitors are LCD monitors, but not all LCD monitors are LEDs. The basic technology of the two is the same, both have two layers of polarized glass, the liquid crystal can both block the light and through the light.
The big difference is the backlight. Standard LCD monitors use a fluorescent backlight, while LED monitors use light-emitting diodes as the backlight. LED displays typically have better image quality.
What is the difference between LED video display and dot matrix LED display?
LED Video Display refers to a monitor that supports moving images, equipped with numerous high-pixel LEDs to provide higher-resolution videos. Those modern billboard seen on Times Square are LED Video Displays.
LED Video Display are more commonly used for large, high-resolution video displays, while dot matrix panels are mainly used for displaying text and animations.
In terms of appearance, the LED video display's LEDs are seamlessly positioned to form a smooth screen, while the LEDs on the dot-matrix panel are arranged in a grid-like pattern with notable spacing.
How is pixel pitch related to resolution?
To conclude, a smaller pixel pitch generally leads to a higher resolution.
Pixel Pitch is the center-to-center distance between adjacent Light Emitting Diode (LED) pixels on an LED screen, typically measured in millimeters (mm). A smaller pixel pitch means that the LED pixels are more densely packed, resulting in a finer display.
Resolution refers to the number of pixels in the horizontal and vertical directions on an LED screen. It is usually expressed as the product of the horizontal pixel count multiplied by the vertical pixel count. For example, 1920x1080 indicates there are 1920 pixels in the horizontal direction and 1080 pixels in the vertical direction.
The relationship between pixel pitch and resolution can be expressed by the following formula:
Resolution = Screen Width (pixels) / Pixel Pitch (mm) Horizontal × Screen Height (pixels) / Pixel Pitch (mm) Vertical.

 Comments
Comments