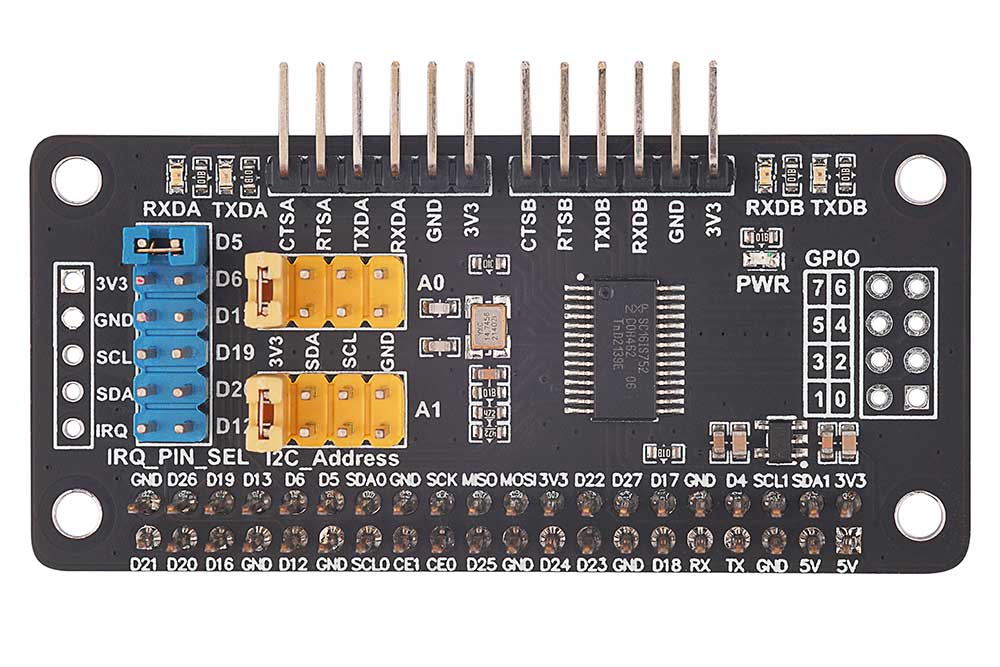
Overview
Based on the Raspberry Pi 40-pin header interface design, this solution is suitable for Raspberry Pi Zero/ Zero W/ Zero WH/ 2B/ 3B/ 3B+/ 4B/ 5. It employs the SC16IS752 chip scheme, enabling the expansion of two serial ports and 8 GPIO simultaneously. The configuration of I2C addresses and selection of interrupt pins are achieved through jumper cap design, ensuring user-friendly operation.
Product Features
- Equipped with SC16IS752 chip, expands 2 serial ports and 8 programmable IO via I2C, without using additional pins.
- By changing the address jumpers, you can connect up to 16 modules, effectively expanding to 32 serial ports.
- Onboard LEDs for serial port transmission and reception, facilitating easy monitoring of the serial port's operational status.
- Reserved I2C control interface for convenient integration with other master controllers.
Product Specifications
| Supply Voltage | 3.3V or 5V |
| Logic Voltage | 3.3V |
| Expansion Chip | SC16IS752 |
| Interface Protocol | I2C |
| Dimensions | 65mm(length) x 30.5mm(width) |
Resource Overview
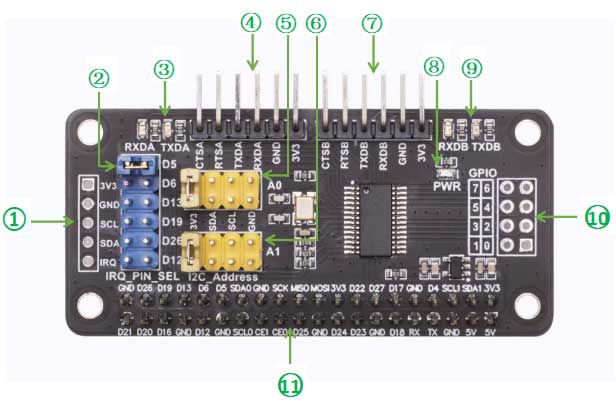
- ① Reserved solder pads for I2C control interface.
- ② Selection of interrupt pin.
- ③ Transmission and reception indicator lights for Serial Port A.
- ④ Header pins for Serial Port A.
- ⑤ I2C address A0 configuration.
- ⑥ I2C address A1 configuration.
- ⑦ Header pins for Serial Port B.
- ⑧ Power indicator light.
- ⑨ Transmission and reception indicator lights for Serial Port B.
- ⑩ Reserved solder pads for GPIO ports.
- ⑪ Raspberry Pi 40-pin female header.
Hardware Interface Configuration Instructions
The Serial Expansion Module exposes all I2C address lines. The addresses of A0 and A1 can be set through the jumper cap. Additionally, 6 interrupt pins are exposed, allowing stacking up to 6 Serial Expansion Modules. In our provided example, the address is set to 0x48, and the interrupt pin is set to D5 (BCM). and set the jumper caps as follows:
* Hardware Connection : Header
* I2C_Address: A0 -> 3V3 IRQ_PIN: IRQ -> D26
* A1 -> 3V3The correspondence between A0/A1 settings and addresses is shown as follows:
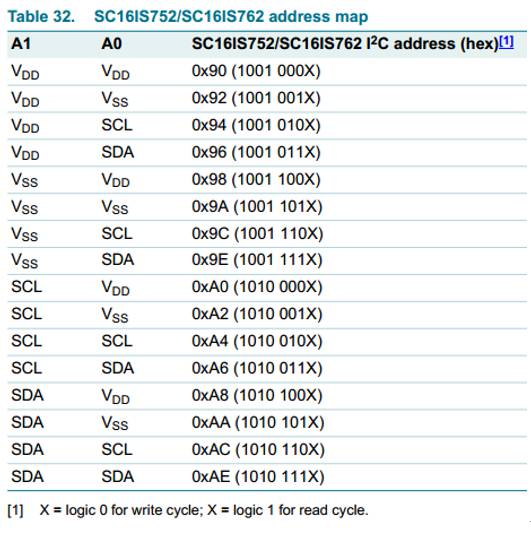
It's clear that the addresses listed in the table are given in 8-bit format. However, in practical operations, I2C addresses are 7 bits. So, you need to shift the address one bit to the right. For example, if you connect both A1 and A0 to VDD, the address given in the table is 0x90 (1001 000X). But in actual usage, the corresponding device address should be 100 1000, which is 0x48. If you want to stack multiple Serial Expansion Modules, you need to set each module to different addresses and use different interrupt pins.
Sample Programs
Since the bookworm system no longer supports the wiringpi library, the example program for this system uses the lgpio library, and for the bullseye system, the wiringpi library version of the example program can be used.
Install wiringpi library:
sudo apt-get install wiringpi
wget https://project-downloads.drogon.net/wiringpi-latest.deb #Raspberry Pi 4B version upgrade
sudo dpkg -i wiringpi-latest.deb
gpio -v #If version 2.52 appears, it means that the installation has been successful
Install lgpio library:
For the bookworm system, the sample program uses the lgpio library. The following is the installation command for the library:
wget https://github.com/joan2937/lg/archive/master.zip
unzip master.zip
cd lg-master
make
sudo make installGenerate device:
sudo nano /boot/config.txt #/boot/firmware/config.txt for bookworm system# addr is set according to the actual combination of A0 A1 jumper caps, the default is 0x48
dtoverlay=sc16is752-i2c,int_pin=26,addr=0x48# If you need to stack multiple Serial Expansion Modules, modify x and 0xyy in the following code according to the combination of your actual jumper caps, and remove #
#dtoverlay=sc16is752-i2c,int_pin=x,addr=0xyy# Reboot the device
sudo rebootExecute after restart:ls /dev/ttySC*
If /dev/ttySC0 and /dev/ttySC1 appear, the configuration is successful; if two Serial Expansion Modules are stacked, /dev/ttySC0, /dev/ttySC1, /dev/ttySC2, /dev/ttySC3 will appear.
Install the serial library in the python environment:
sudo apt-get install python3-serialRaspberry Pi I2C Configuration
Start the Raspberry Pi system configuration:
sudo raspi-configEnable I2C interface:
Interfacing Options -> I2C -> Yes
Reboot the device
sudo rebootCheck out the enabled I2C devices:
ls /dev/i2c* #will print out:"/dev/i2c-1"
Install the I2C library:
sudo apt install i2c-toolsInstall python's smbus:
sudo apt install python-smbusDetect the address of the device mounted on the I2C bus:
sudo i2cdetect -y -a 1Execute the I2C interface sample program
Python:
For the bookworm system, if you are using a Raspberry pi 4B, you will need to change PIN_NUM_START = 625 to PIN_NUM_START = 578.
Enter the python directory:
cd /home/pi/Serial_Expansion_Module/demo_codes/raspberry_p/pythonExecute:
sudo python3 sc16is752.pyC:
For the bookworm system, if you are using a Raspberry pi 4B, change #define PIN_START 625 to #define PIN_START 578 in sc16is752.h.
Enter the c directory:
cd /home/pi/Serial_Expansion_Module/demo_codes/raspberry_pi/cExecute:
make clean
make
sudo ./mainDemo Code Explanation
Wiring Instructions:
TXDA----RXDB
RXDA----TXDB
The demo codes is for the operation when only one Serial Expansion Module is inserted. First, complete the initialization of the serial port and GPIO, configure GPIO0~GPIO3 as outputs, and configure GPIO4~GPIO7 as inputs, and then enter the loop steps with a cycle of about 1 second: ttySC0 sends the character "Hello word", ttySC1 sends the character "www.seengreat.com", then reads the content of the characters received by ttySC0 and ttySC1 and prints it, then GPIO0~GPIO3 output the out_val level and read the input level of GPIO4~GPIO7 , the value of out_val is reversed once in each loop.
The serial device symbols are /dev/ttySC0 and /dev/ttySC1, GPIO is controlled by sysfs. For non-bookworm systems, it will generate gpiochip496 in the /sys/class/gpio file path, and GPIO0~GPIO7 on the module correspond to gpio496~gpio503.If two Serial Expansion Module are stacked, gpiochip488 will be added under the /sys/class/gpio file path, and GPIO0~GPIO7 on the second module correspond to gpio488~gpio495.
For the Raspberry pi 5 on the bookworm system, it will generate gpiochip625 in the /sys/class/gpio file path, and GPIO0~GPIO7 on the module corresponds to gpio625 ~gpio632. At the same time, users need to modify the demo codes to use the GPIO pins of the second module.
Resources
Demo Codes for bullseye system
Demo Codes for bookworm system
Data Sheet
