
Overview
Thermal Camera MLX90642-D45(45 ° × 35°) or Thermal Camera MLX90642-D110(110 ° × 75°) is a far-infrared thermal sensor array designed with Melexis MLX90642. With a resolution of 32*24, it provides great performance for applications that do not require high-resolution images or high frame rate, and provides a cost-effective alternative to more expensive high-end infrared thermal camera. Typical applications for the MLX90642 include fire protection systems, intelligent buildings, Intelligent lighting, IP/surveillance cameras, HVAC equipment and vehicle seat occupancy detection.
This product provides demo codes based on Raspberry Pi platform. The demo codes is divided into C and python versions, both of which include thermal image display function.
Specifications
- The working voltage is 3.3v/5v
- I2C interface communication, the highest speed can reach 1MHz
- Noise Equivalent Temperature
- Difference (NETD) is 0.065K RMS @ 2Hz refresh rate
- Support 2Hz~16Hz refresh rate
- The field of view is 45 ° × 35° or 110 ° × 75°
- The temperature measuring range is -40 ℃ ~ 260 ℃
- Dimensions: 20mm(length) x 18mm(width)
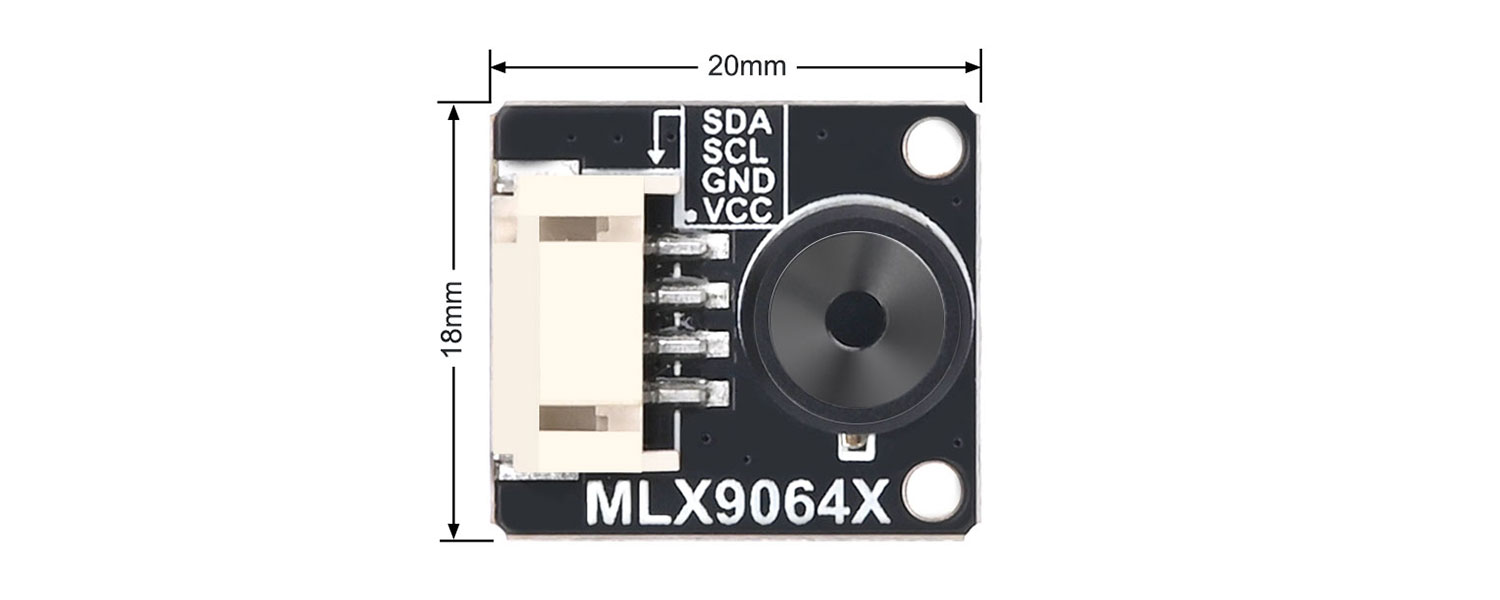
MLX90642
I2C Communication:The communication method of MLX90642 sensor is I2C bus, the default address of the device is 0X66, and the highest speed of its I2C interface can reach 1MHz.
Bad Pixels: The original manufacturer of the sensor allows less than 4 bad pixels when the sensor leaves the factory, so the module may have a certain probability of having bad pixels, but each bad pixel is marked in the EEPROM table. For this, the original manufacturer's suggestion is to use the average value of adjacent pixels instead.
Global Shutter Readout:All pixels of the global shutter expose and end exposure simultaneously, ensuring the entire sensor captures a complete thermal image at the exact same moment. It can eliminate the rolling shutter effect, output distortion-free thermal images, and provide more reliable temperature data. It enables more accurate capture of instantaneous temperature changes (e.g., circuit short-circuit sparks, laser processing spots) without motion blur.The global shutter supports higher frame rates, and combined with its synchronous exposure feature, it is suitable for high-speed dynamic analysis.In multispectral fusion systems (e.g., visible light + infrared), the global shutter can achieve precise temporal synchronization with other sensors, improving data alignment accuracy. However, synchronous exposure requires a more powerful circuit drive and results in slightly higher power consumption.
Usage
Module and Raspberry Pi Connection Instructions
Notice:
1. Please check the power supply before power on to prevent reverse connection, and do not plug and unplug with power while working
2. Do not touch the core components with both hands directly when the product is working, and do a good job in electrostatic protection
3. It is recommended not to use too long cables to connect the module, otherwise it will easily lead to EEPROM write error and failure
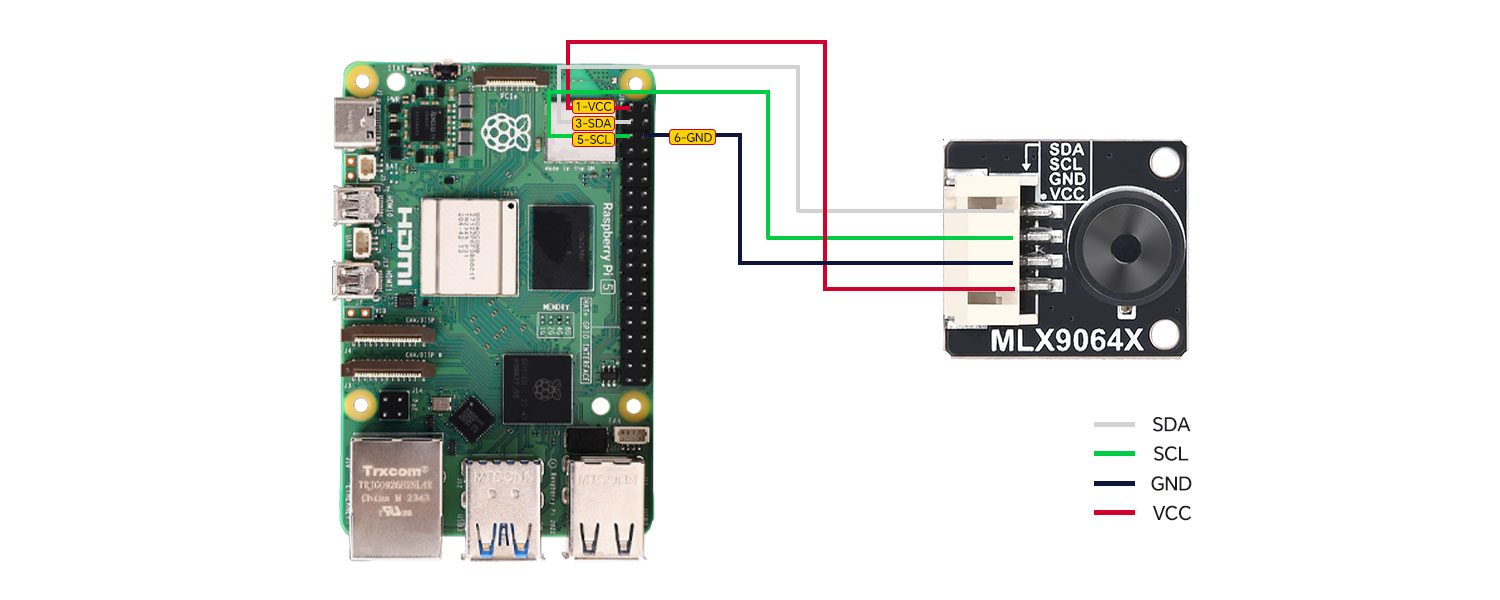
| Module Pins | Raspberry Pi BOARD Number | Function Name | Wiring Instructions |
|---|---|---|---|
| GND | 6 | GND | GND |
| VCC | 1 | 3.3V | VCC |
| SDA | 3 | SDA.1 | I2C Data |
| SCL | 5 | SCL.1 | I2C Clock |
Demo Codes
This product provides demo codes based on Raspberry Pi mainboard, which is divided into two programming languages: C++ and python. For the convenience of users, Melexis provides a C++ driver library. The underlying I2C driver in the code is implemented by the I2C Driver related functions in the library, and the acquisition of temperature data is also implemented by the API related functions in the library. The C++ version code uses the CImg image processing library for image processing and display, while the python version code uses the PIL (Python Image Library) library and the Tkinter module.
IMLX90642 Driver Library
The library is provided by Melexis and is divided into two parts: I2C driver and API function. When using the project normally, the code should contain the following 4 files:
MLX90642.h – Header file containing the definitions of MLX90642 API-related functions
MLX90642_depends.h – Header file containing the definitions of I2C read/write-related functions
MLX90642.cpp – File containing the implementations of MLX90642 API functions
MLX90642_LINUX_I2C_Driver.cpp contains the I2C read/write functions for MLX90642, which are developed based on the Raspberry Pi platform.
Raspberry Pi I2C Configuration
Start the Raspberry Pi system configuration:
sudo raspi-config
Enable I2C interface:
Interfacing Options -> I2C -> Yes
Modify I2C communication baud rate (recommended to be set to 500000 or above):
sudo nano /boot/config.txt(for bullseye system)
or
sudo nano /boot/firmware/config.txt(for bookworm system)
dtparam=i2c1_baudrate=800000
save and exit
sudo reboot
Check enabled I2C devices:
ls /dev/i2c* # at this time, it will print out: "/dev/i2c-1"
Install the I2C bus tools:
sudo apt install i2c-tools
Detect the device address mounted on the I2C bus:
sudo i2cdetect -y -a 1
Execute the C++ Demo Codes
Enter the C++ directory (here users can modify the path according to their actual project location):
cd /home/pi/mlx90642/cpp
sudo make clean
sudo make
sudo ./mainNote:If the error message "x11/xlib. h nosuch file or directory" appears when executing "sudo make", install X11 first. The command is:
sudo apt -get install libx11-dev
If the problem has not been solved, enter the command to check which components have not been installed: apt-cache search x11-dev, and then install them in sequence. For example, after entering this command, the following contents appear:
libgl1-mesa-swx11-dev - A free implementation of the OpenGL API -- development files
libghc6-x11-dev - Haskell X11 binding for GHC
libgtkglextmm-x11-dev - C++ wrapper for the OpenGL Extension to GTK (development files)
libx11-dev - X11 client-side library (development headers)
Then use the following commands to install in turns:
sudo apt-get install libx11-dev
sudo apt-get install libgtkglextmm-x11-dev
sudo apt-get install libghc6-x11-dev
sudo apt-get install libgl1-mesa-swx11-devExecute the python Demo Codes
Firstly, install the python library:
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install python3-pip
sudo apt-get install python3-pil python3-pil.imagetk
sudo apt-get install python3-numpyEnter the python directory (here users can modify the path according to their actual project location):
cd /home/pi/mlx90642/python
cd lib
sudo make clean
sudo make
cd ..
sudo python3 mlx90642.pyThe files in the lib folder are used to generate the dynamic library mlx90642. so that can be called by the python environment, MiSans-Light.ttf is the font file used for temperature display characters, and usr_api.cpp, usr_api.h are built in the MLX90642 driver library on the application layer file. The user can directly call the function definition in the usr_api.cpp file to realize the initialization of the MLX90642 device and the acquisition of temperature data.
Resources
Data Sheet
